Economics
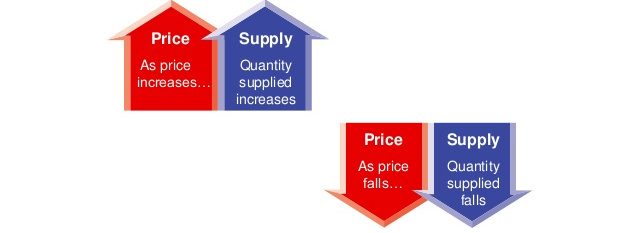
The Law of Supply is a fundamental principle in economics that states:
- As the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied also increases.
- As the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases.
This happens because higher prices make production more profitable, encouraging businesses to produce and sell more. Conversely, when prices drop, suppliers may reduce production because it becomes less profitable.
There are two major types of credit—using credit cards and borrowing directly from a financial institution. Although they differ in their services, they all charge interest on the funds they lend. In this section, you’ll learn about financial institutions, charge accounts, and credit cards—and why you should be aware of the high interest rates they sometimes charge.
We all have an understanding of the concept of income on an individual level and what our own income is. But how should we measure the income of a whole economy? What is the relation between our income and the value of what we produce? To find the nation’s income do we just add up the incomes of the household, business, and government sectors? And how does the rest-of-the-world enter the picture? What does the nation spend its income on, and what does it save? How does savings relate to investment?
In the complex world of business and manufacturing, one fundamental principle stands out as a critical driver of competitive advantage: economies of scale. This concept reveals a powerful relationship between production size and cost efficiency, demonstrating that larger operations can significantly reduce per-unit production costs. By understanding and leveraging economies of scale, companies can transform their economic landscape, creating more profitable and sustainable business models.
Inflation is one of the most significant economic phenomena that affects individuals, businesses, and governments. It represents the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, reducing purchasing power over time. While moderate inflation is a sign of a growing economy, excessive inflation can have severe consequences, including reduced savings, increased cost of living, and economic instability. This article explores the causes of inflation, its effects on various sectors, and strategies to mitigate its impact.